Understanding Lymphedema: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Lymphedema is a chronic condition caused by a blockage in the lymphatic system, leading to swelling, often in the arms or legs. Learn how early recognition, lifestyle changes, and proper care can help manage symptoms and improve daily comfort and mobility.

What is lymphedema and how does it affect the lymphatic system?
Lymphedema is a condition that results from an impairment in the lymphatic system’s ability to drain excess fluid from tissues. The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and nodes that helps remove waste, bacteria, and other substances from the body’s tissues. When this system is compromised, fluid accumulates in the affected area, leading to swelling, discomfort, and potential complications.
In lymphedema, the lymphatic vessels may be damaged, underdeveloped, or blocked, preventing the normal flow of lymph fluid. This can cause a buildup of protein-rich fluid in the tissues, leading to chronic swelling and potential tissue changes over time. The affected area may feel heavy, tight, or painful, and the skin can become thickened or develop a leathery texture.
What are the common causes of lymphedema?
Lymphedema can be categorized into two main types: primary and secondary. Understanding the underlying causes can help in developing appropriate treatment strategies and preventive measures.
Primary lymphedema is a rare, inherited condition caused by abnormalities in the development of the lymphatic system. It can be present at birth or develop later in life, often during puberty or early adulthood. Genetic mutations affecting the formation or function of lymphatic vessels are responsible for this type of lymphedema.
Secondary lymphedema, which is more common, occurs as a result of damage to the lymphatic system. Common causes include:
-
Cancer treatments: Surgery, particularly when lymph nodes are removed, and radiation therapy can damage lymphatic vessels and nodes.
-
Infections: Certain parasitic infections, such as lymphatic filariasis, can obstruct lymph flow.
-
Trauma: Injuries, burns, or scarring can damage lymphatic vessels.
-
Obesity: Excess weight can put pressure on lymphatic vessels, impeding proper drainage.
-
Chronic venous insufficiency: This condition can lead to secondary lymphedema in the legs.
What lifestyle tips can help with daily lymphedema management?
Managing lymphedema effectively requires a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle modifications. Incorporating these daily habits can help control swelling and reduce discomfort:
-
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can exacerbate lymphedema symptoms, so following a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise is crucial.
-
Exercise regularly: Gentle exercises, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can help stimulate lymph flow and reduce swelling.
-
Protect the affected area: Avoid injuries, cuts, and burns to prevent infections. Use sunscreen and insect repellent when outdoors.
-
Wear compression garments: Custom-fitted compression sleeves or stockings can help prevent fluid buildup during daily activities.
-
Practice good skin care: Keep the affected area clean and moisturized to prevent skin breakdown and infections.
-
Elevate the affected limb: When possible, elevate the swollen limb above heart level to encourage fluid drainage.
-
Stay hydrated: Proper hydration supports overall lymphatic function.
-
Avoid tight clothing or jewelry: These can restrict lymph flow and worsen swelling.
What techniques and therapies are used to treat lymphedema?
Several specialized techniques and therapies can be employed to manage lymphedema effectively:
-
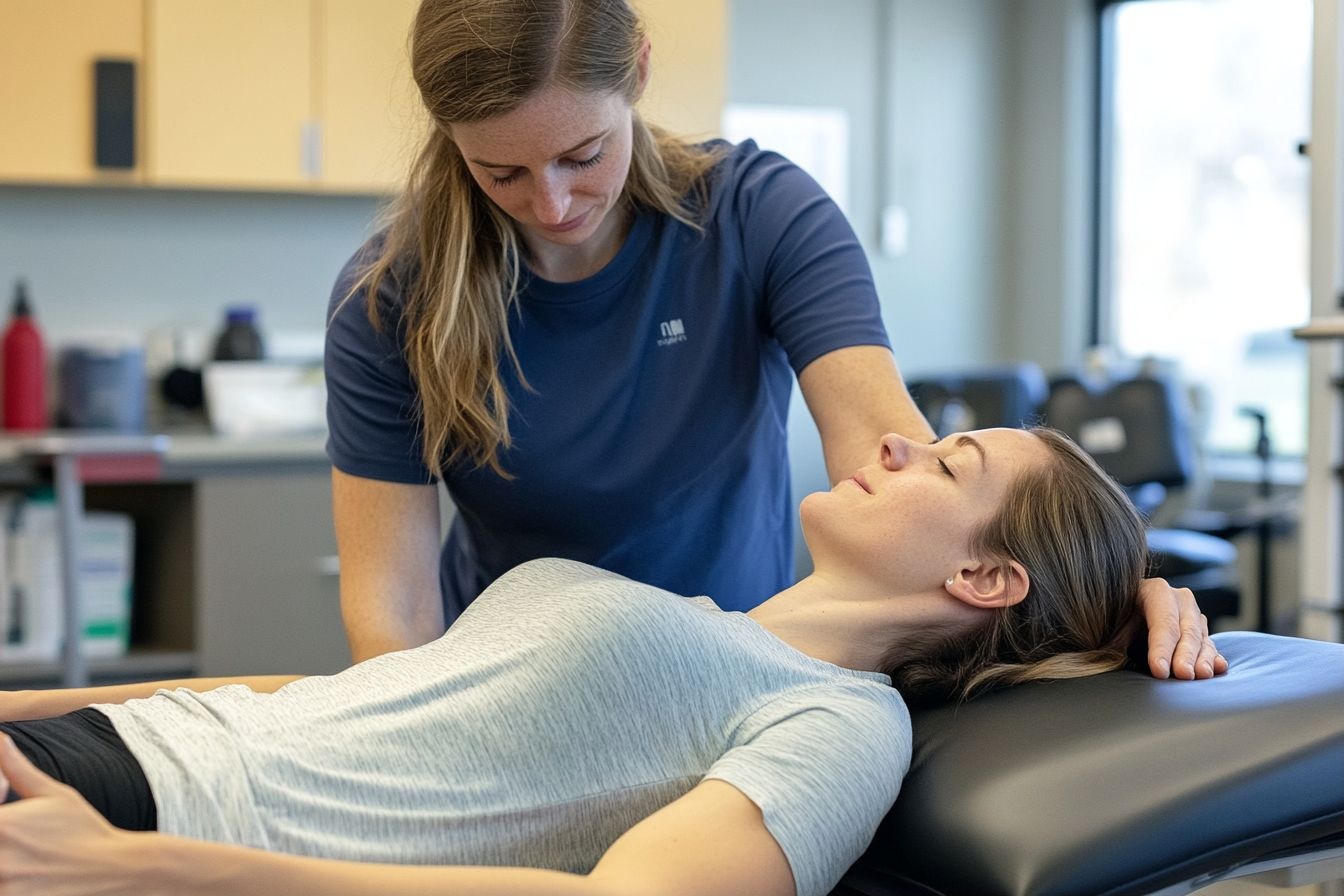
Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT): This comprehensive approach combines several treatments, including manual lymph drainage, compression therapy, exercise, and skin care.
-
Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD): A gentle massage technique that stimulates lymph flow and redirects fluid to functioning lymph vessels.
-
Compression therapy: The use of bandages, garments, or pneumatic compression devices to apply pressure and prevent fluid accumulation.
-
Exercise therapy: Specific exercises designed to improve lymph flow and strengthen affected areas.
-
Kinesio taping: Application of elastic therapeutic tape to create channels for improved lymph drainage.
-
Low-level laser therapy: Use of low-level lasers to stimulate lymph flow and reduce inflammation.
-
Surgery: In some cases, surgical interventions such as lymph node transfer or lymphovenous anastomosis may be considered to improve lymphatic drainage.
-
Pneumatic compression devices: These mechanical pumps apply pressure to affected limbs, encouraging fluid movement.
Lymphedema management often requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving collaboration between healthcare professionals such as lymphedema therapists, physical therapists, and physicians specializing in vascular or lymphatic disorders.
While there is no cure for lymphedema, early diagnosis and proper management can significantly improve symptoms and prevent complications. By understanding the causes of lymphedema, implementing lifestyle changes, and utilizing appropriate therapies, individuals with this condition can maintain a good quality of life and minimize the impact of symptoms on their daily activities.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.