Key Considerations in the Use of Levothyroxine as Prescribed
Levothyroxine is a medication commonly used under medical supervision to support thyroid hormone levels. Its use typically involves regular dosage evaluations, timing considerations, and clinical monitoring. Any adjustments or related care decisions are made by a licensed healthcare provider based on individual health needs.

What is levothyroxine and how does it work?
Levothyroxine is a synthetic form of thyroxine (T4), the primary hormone produced by the thyroid gland. When the thyroid cannot produce adequate amounts of this essential hormone, levothyroxine serves as a replacement to restore normal metabolic function. The medication works by mimicking the action of natural thyroid hormone, regulating cellular metabolism, energy production, and various bodily functions including heart rate, body temperature, and protein synthesis.
Once absorbed into the bloodstream, levothyroxine is converted to triiodothyronine (T3), the more active form of thyroid hormone. This conversion process occurs primarily in the liver and other tissues throughout the body. The medication helps restore the delicate balance of thyroid hormones that control metabolism, supporting normal growth, development, and cellular function.
How should I take levothyroxine for best results?
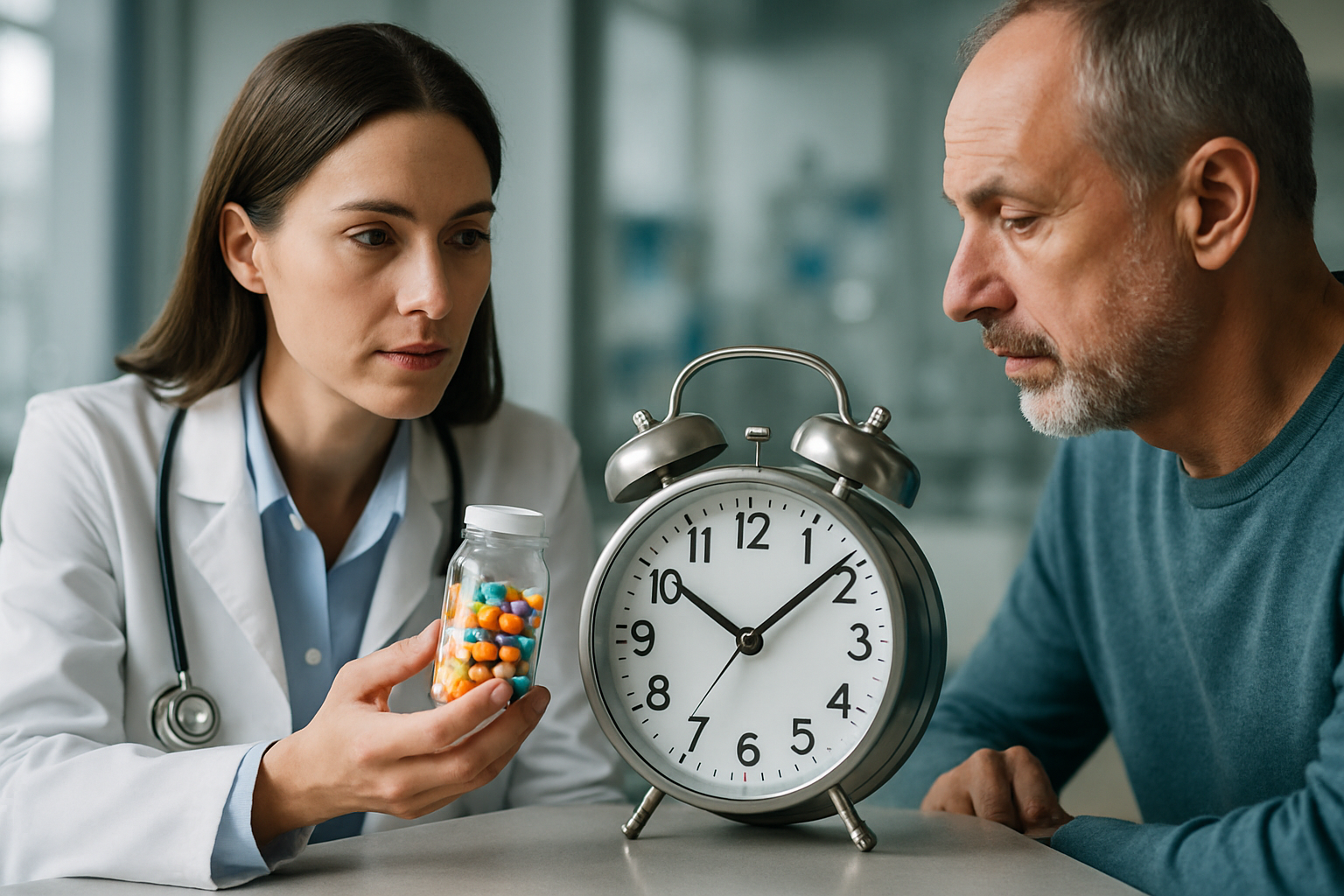
Taking levothyroxine correctly is crucial for achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes. The medication should be taken on an empty stomach, typically 30 to 60 minutes before breakfast, with a full glass of water. This timing ensures maximum absorption and prevents interference from food or other substances.
Consistency in timing is equally important. Taking levothyroxine at the same time each day helps maintain steady hormone levels in the bloodstream. Many patients find success taking their medication immediately upon waking, establishing a reliable routine that becomes second nature. If a morning dose is missed, it can generally be taken later in the day, but it should be at least four hours away from meals and other medications.
What factors can affect levothyroxine absorption?
Several factors can significantly impact how well your body absorbs levothyroxine, potentially reducing its effectiveness. Food, particularly high-fiber meals, calcium-rich foods, and coffee, can interfere with absorption when consumed too close to medication timing. Iron supplements, calcium carbonate, and antacids containing aluminum or magnesium should be taken at least four hours apart from levothyroxine.
Certain medical conditions can also affect absorption, including celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and gastric bypass surgery. Age-related changes in stomach acid production may reduce absorption efficiency in older adults. Additionally, some medications like proton pump inhibitors, which reduce stomach acid, can impact how well levothyroxine is absorbed into the system.
Are there any side effects of taking levothyroxine?
When properly dosed and monitored, levothyroxine typically produces minimal side effects since it replaces a hormone naturally produced by the body. However, taking too much can cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including rapid heartbeat, anxiety, tremors, excessive sweating, weight loss, and difficulty sleeping. These symptoms usually indicate the need for dosage adjustment rather than discontinuation of the medication.
Some patients may experience temporary hair loss during the initial months of treatment as the body adjusts to hormone replacement. Allergic reactions to levothyroxine are rare but can occur, typically involving ingredients in the tablet formulation rather than the active hormone itself. Switching to a different brand or formulation often resolves such issues under medical supervision.
Thyroid Treatment Landscape in the United States
The United States has established comprehensive guidelines for thyroid treatment through organizations like the American Thyroid Association and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. These guidelines emphasize individualized treatment approaches, with starting doses typically ranging from 25 to 100 micrograms daily, depending on patient age, weight, cardiac status, and severity of hypothyroidism. Many healthcare systems now offer specialized thyroid clinics and endocrinology services to provide comprehensive care for complex cases.
Recent advances in thyroid treatment include the availability of liquid formulations and soft gel capsules that may offer improved absorption for certain patients. Some medical centers also provide combination therapy options, though levothyroxine monotherapy remains the standard of care for most patients with hypothyroidism.
How can I monitor the effectiveness of my levothyroxine treatment?
Regular monitoring through blood tests is essential for ensuring levothyroxine treatment effectiveness. The primary marker is thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which should be checked 6 to 8 weeks after starting treatment or any dose adjustment. Once stable, most patients require TSH monitoring every 6 to 12 months, though individual needs may vary.
Target TSH levels typically range from 0.4 to 4.0 mIU/L for most adults, though your healthcare provider may establish more specific targets based on your individual circumstances. Some patients may also require periodic monitoring of free T4 levels, particularly if symptoms persist despite normal TSH values. Keeping a symptom diary can help track improvements in energy, mood, weight management, and other thyroid-related symptoms between laboratory evaluations.
Successful levothyroxine treatment requires partnership between patients and healthcare providers, with attention to proper administration, regular monitoring, and open communication about symptoms and concerns. With appropriate medical supervision and adherence to treatment guidelines, most patients achieve excellent outcomes and symptom resolution.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.