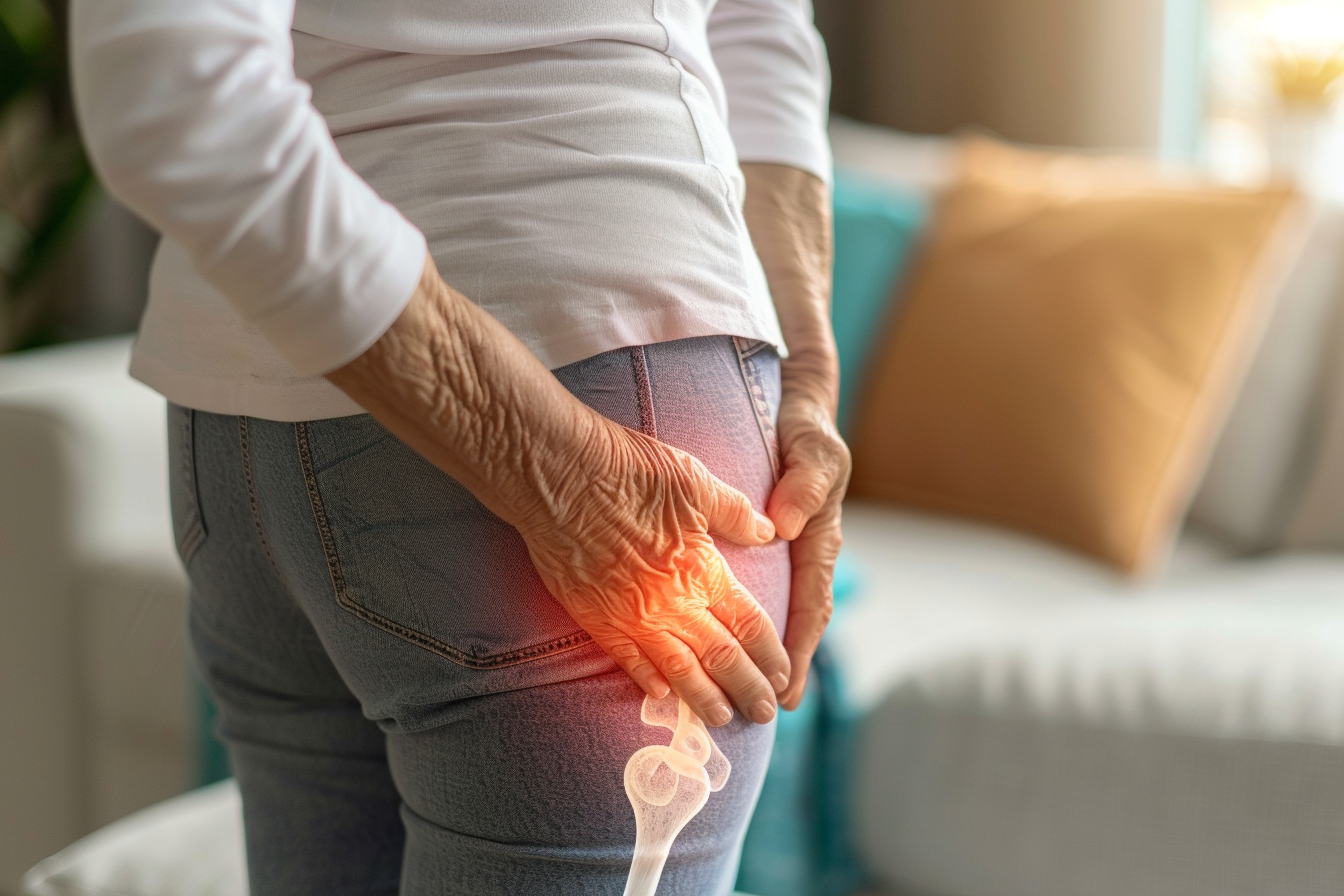
Explore Effective Osteoarthritis Treatments
Osteoarthritis can impact mobility and daily comfort but many treatment options now exist to ease symptoms and improve quality of life. From lifestyle changes to medical therapies people are finding relief and support through approaches tailored to their needs.
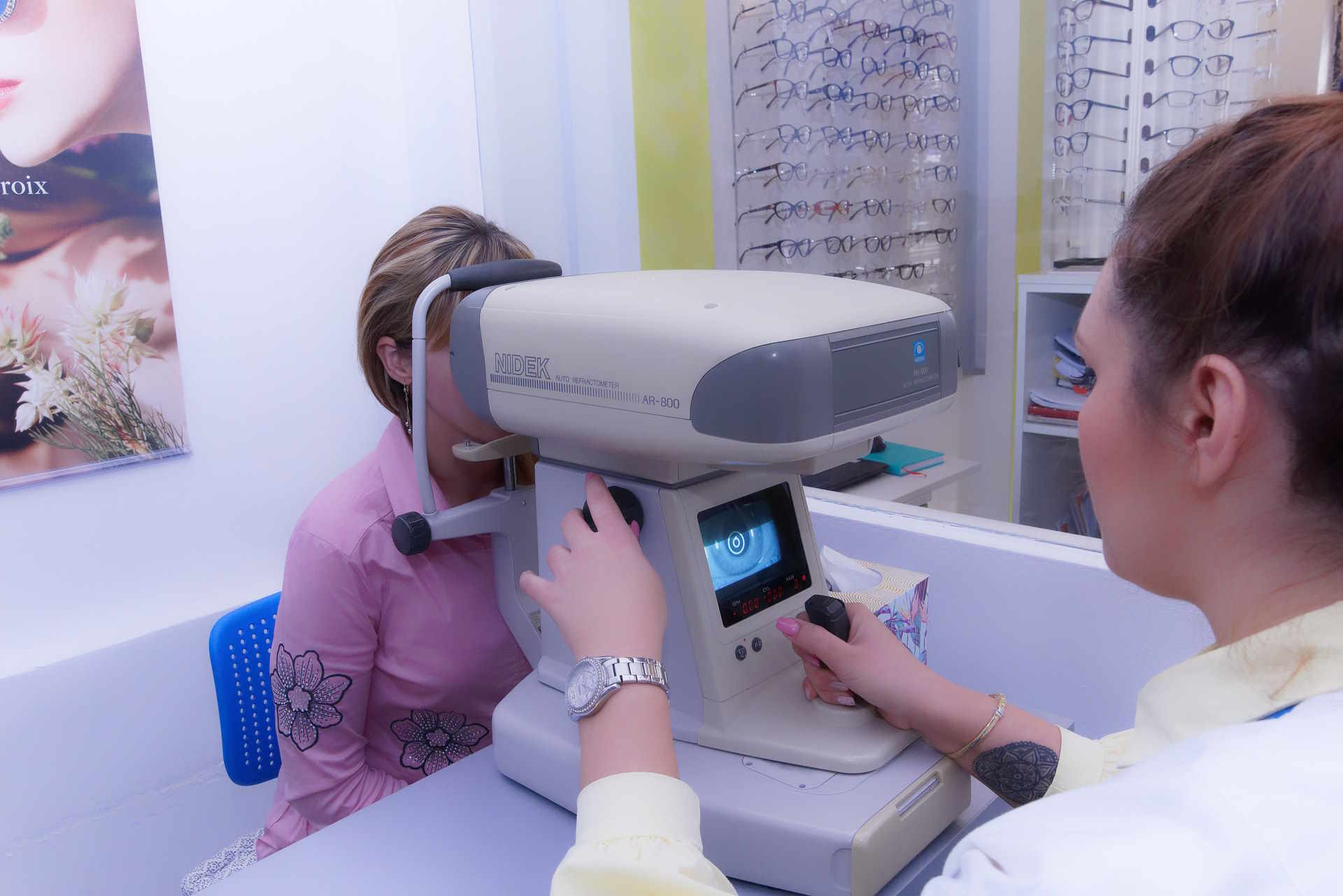
Understanding Treatment Options Available for Osteoarthritis Relief
Osteoarthritis treatment typically follows a multifaceted approach, combining various strategies to address pain, improve joint function, and enhance quality of life. The treatment plan often starts with conservative measures and may progress to more invasive options if symptoms persist or worsen. Most healthcare providers recommend starting with non-surgical treatments before considering surgical interventions.
Conservative treatments include weight management, regular exercise, physical therapy, and assistive devices. Weight loss reduces stress on weight-bearing joints such as knees and hips, potentially slowing disease progression. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and walking strengthen the muscles around affected joints, improving stability and function. Physical therapy teaches specific exercises to improve range of motion and strengthen supporting muscles. Assistive devices such as braces, shoe inserts, canes, or walkers can help reduce joint stress during daily activities.
When these approaches aren’t sufficient, healthcare providers may recommend medications, injections, or in severe cases, surgical interventions. The appropriate treatment combination depends on individual factors including age, overall health, affected joints, and symptom severity.
Painkillers for Osteoarthritis: Finding Effective Relief
Medication plays a crucial role in managing osteoarthritis pain and improving function. Different types of painkillers target various aspects of pain and inflammation associated with the condition.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is often the first medication recommended for mild to moderate osteoarthritis pain. It helps reduce pain but doesn’t address inflammation. For those who don’t respond adequately to acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) and naproxen sodium (Aleve) can reduce both pain and inflammation. These are available over-the-counter in lower strengths or by prescription in higher doses.
For more severe pain, doctors may prescribe stronger medications such as tramadol or other opioids, though these carry risks of dependency and side effects. Duloxetine (Cymbalta), an antidepressant, is sometimes prescribed for chronic musculoskeletal pain, including osteoarthritis.
Topical treatments applied directly to the skin over affected joints can also provide relief. These include NSAIDs in gel or cream form (like diclofenac gel), capsaicin cream, or lidocaine patches. These typically have fewer side effects than oral medications since they work locally rather than throughout the entire body.
How to Treat Osteoarthritis Naturally: Lifestyle Approaches
Many people with osteoarthritis seek natural approaches to complement conventional treatments or to avoid medication side effects. Evidence suggests several natural methods can help manage symptoms effectively.
Dietary changes can play a significant role in managing osteoarthritis. Anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), nuts, olive oil, fruits, and vegetables may help reduce inflammation throughout the body. Some research suggests that specific supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate might help slow cartilage deterioration and reduce pain, though scientific evidence remains mixed. Omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and ginger have also shown promise in reducing inflammation and osteoarthritis pain in some studies.
Mind-body techniques can help manage pain perception and improve quality of life. These include practices like yoga, tai chi, meditation, and acupuncture. Tai chi and yoga combine gentle movements with mindfulness, potentially improving joint function, balance, and pain management. Regular practice of these techniques can also help reduce stress, which often exacerbates pain perception.
Heat and cold therapy represent simple yet effective natural approaches. Applying heat increases blood flow and relaxes stiff joints and muscles, while cold therapy reduces inflammation and numbs acute pain. Alternating between the two can provide significant relief for many people.
Advanced Treatments and Interventions for Severe Osteoarthritis
When conservative measures and medications don’t provide adequate relief, more advanced interventions may be necessary. These approaches target specific joint issues and can significantly improve function and quality of life.
Injection therapies deliver medication directly to affected joints. Corticosteroid injections reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief, typically lasting several weeks to months. Hyaluronic acid injections (viscosupplementation) involve injecting a gel-like substance that acts as a lubricant and shock absorber in the joint, particularly beneficial for knee osteoarthritis. More recently, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections have emerged as a treatment option, using a concentration of a patient’s own platelets to accelerate healing, though research on their effectiveness continues.
For severe osteoarthritis that significantly impacts quality of life, surgical options might be considered. Joint replacement surgery (arthroplasty) removes damaged joint surfaces and replaces them with metal and plastic components. This procedure is most commonly performed on knees and hips with high success rates. Other surgical options include osteotomy (realigning bones to shift pressure from damaged areas) and joint fusion (arthrodesis) for joints like ankles, wrists, or spine.
Newer regenerative medicine approaches like stem cell therapy show promise in early research but remain experimental. These treatments aim to regenerate damaged cartilage tissue rather than simply managing symptoms.
Creating a Comprehensive Osteoarthritis Management Plan
Managing osteoarthritis effectively typically requires a personalized, comprehensive approach that combines multiple treatment strategies. Working closely with healthcare providers to develop and adjust this plan over time is essential for optimal outcomes.
A comprehensive management plan often includes regular exercise tailored to individual capabilities, weight management strategies, appropriate use of medications and supplements, physical therapy, and proper joint protection techniques during daily activities. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers allows for monitoring disease progression and treatment effectiveness, with adjustments made as needed.
Patient education plays a crucial role in successful management. Understanding how to protect joints during daily activities, recognize worsening symptoms, and implement self-care strategies empowers individuals to take an active role in their treatment. Support groups and community resources can provide valuable emotional support and practical tips for living well with osteoarthritis.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.