Common Vitamins That May Support Nutritional Needs in Diabetes
Certain vitamins and minerals are commonly discussed in relation to supporting the nutritional needs of individuals with diabetes. Nutrients like vitamin D, vitamin B12, and magnesium are often reviewed for their general roles in overall health, as part of broader dietary management approaches.
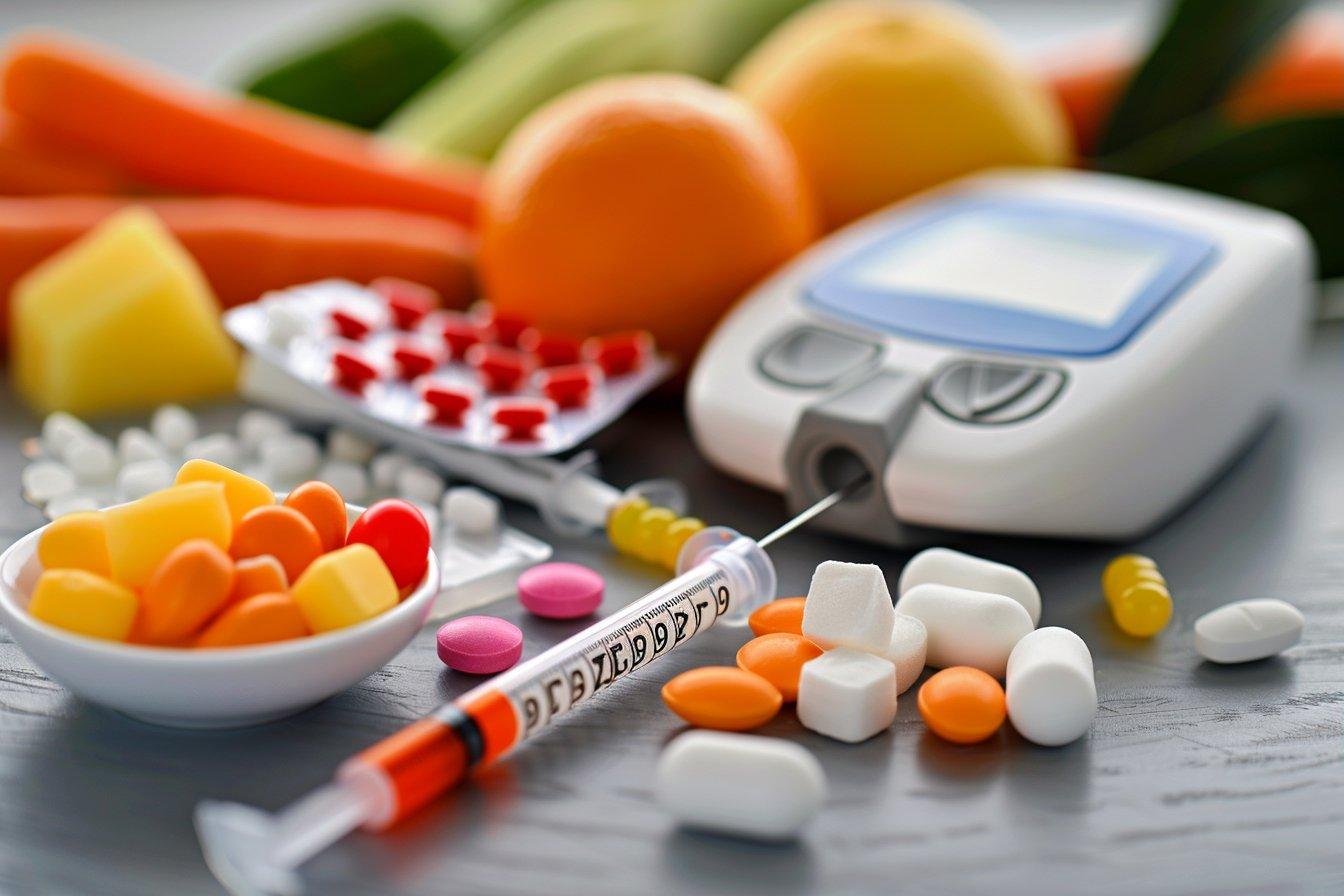

What role do vitamins play in diabetes management?
Vitamins are essential micronutrients that play various roles in maintaining overall health. For individuals with diabetes, certain vitamins may help support metabolic functions, potentially contribute to better blood sugar control, and assist in preventing or managing some diabetes-related complications. However, it’s important to note that vitamins are not a substitute for prescribed diabetes treatments or a healthy lifestyle. They should be viewed as part of a comprehensive diabetes management plan.
Which vitamin is most commonly associated with diabetes?
Vitamin D is perhaps the most frequently discussed vitamin in relation to diabetes. This nutrient plays a crucial role in calcium absorption and bone health, but research has also suggested potential links between vitamin D levels and insulin sensitivity. Some studies have indicated that adequate vitamin D levels may be associated with better blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between vitamin D and diabetes management.
Can B vitamins help with blood sugar control?
B vitamins, particularly B12, B6, and B1 (thiamine), are often of interest in diabetes management. These vitamins play important roles in energy metabolism and nerve function. Vitamin B12 is especially crucial, as some diabetes medications may lower B12 levels over time. While B vitamins are essential for overall health, their direct impact on blood sugar control is still being studied. Some research suggests that adequate B vitamin intake may help support nerve health in individuals with diabetes.
What are the potential benefits of magnesium for diabetics?
Magnesium, while technically a mineral rather than a vitamin, is frequently discussed in the context of diabetes nutrition. This essential nutrient is involved in numerous bodily processes, including glucose metabolism and insulin function. Some studies have suggested that adequate magnesium intake may be associated with better insulin sensitivity and potentially lower risk of type 2 diabetes. However, as with other nutrients, more research is needed to fully understand magnesium’s role in diabetes management.
Are there specific vitamins recommended for seniors with diabetes?
Seniors with diabetes may have unique nutritional needs due to age-related factors and potential medication interactions. While individual needs vary, some vitamins and minerals often recommended for seniors with diabetes include:
- Vitamin D: Important for bone health and potentially insulin sensitivity.
- Vitamin B12: Crucial for nerve health and potentially at risk of deficiency in older adults.
- Calcium: Essential for bone health, especially in older adults.
- Magnesium: Potentially beneficial for insulin function and overall health.
It’s important to note that these recommendations are general, and seniors should consult their healthcare providers for personalized nutrition advice.
How should individuals approach vitamin supplementation for diabetes?
While vitamins and minerals play important roles in overall health, it’s crucial to approach supplementation carefully, especially for individuals managing diabetes. Here are some key considerations:
- Consult healthcare providers: Always discuss vitamin supplementation with a doctor or registered dietitian before starting any new regimen.
- Focus on food first: Aim to obtain vitamins and minerals from a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Be aware of interactions: Some vitamins and supplements may interact with diabetes medications or affect blood sugar levels.
- Avoid megadoses: Taking excessive amounts of vitamins can be harmful and may interfere with diabetes management.
- Regular monitoring: If supplementing, work with healthcare providers to monitor vitamin levels and overall health regularly.
| Nutrient | Potential Benefits for Diabetes | Food Sources | Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for Adults |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | May support insulin sensitivity | Fatty fish, fortified dairy, sunlight exposure | 600-800 IU |
| Vitamin B12 | Supports nerve health | Animal products, fortified foods | 2.4 mcg |
| Magnesium | May aid insulin function | Nuts, seeds, whole grains, leafy greens | 310-420 mg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) | Supports energy metabolism | Whole grains, nuts, beans | 1.1-1.2 mg |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
In conclusion, while certain vitamins and minerals may potentially support the nutritional needs of individuals with diabetes, it’s crucial to approach supplementation as part of a comprehensive diabetes management plan. A balanced diet, regular exercise, proper medication management, and ongoing consultation with healthcare providers remain the cornerstones of effective diabetes care. Vitamins should be viewed as potential supportive elements rather than primary treatments for diabetes.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
The shared information of this article is up-to-date as of the publishing date. For more up-to-date information, please conduct your own research.